| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | May-14-25 |
Read Next
- Difference Between Mainboard IPO and SME IPO
- Bharat Coking Coal IPO Allotment Status Check Online: GMP, Subscription, Price, and & Key Highlights
- Bharat Coking Coal IPO Day 2: Subscription at 33x, GMP Jumps to ₹10.85
- What is Pre-IPO Investing?
- What is Prospectus?
- ICICI Prudential AMC IPO Allotment Status: Check Latest GMP, Steps to Verify Status
- ICICI Prudential AMC IPO Day 2: Subscription at 2.02x, GMP Jumps to ₹268
- What is SME IPO?
- Meesho IPO Allotment Status: Check Latest GMP, Steps to Verify Status
- Aequs Ltd. IPO Allotment Status: Check Latest GMP, Steps to Verify Status
- Meesho IPO: 8.26x Subscription on Day 2, GMP ₹44.5 & Key Details
- Aequs Ltd. IPO GMP Today: Subscription Status, Allotment Dates & Details
- What is a Deemed Prospectus?
- What is Oversubscription in IPOs?
- Groww (Billionbrains Garage Ventures Ltd.)IPO Allotment Status, GMP, Subscription & Listing Date
- Top 10 Most Highest Subscribed IPOs in India
- Lenskart Solutions IPO Allotment Status, GMP, Subscription & Listing Date
- Studds Accessories IPO Allotment Status: Check Latest GMP, Steps to Verify Status
- Top 10 Largest IPOs in India
- What is a Confidential IPO Filing?
OFS vs IPO: Key Differences and Benefits

In today’s time, if you want to invest in the stock market, then you need to understand how companies bring their shares to the public. There are two main ways of doing this: IPO (Initial Public Offering) and OFS (Offer for Sale). An IPO is when a company sells its shares to the public for the first time, through which the company raises new capital. On the other hand, in OFS, the promoters or big investors of an already listed company sell their share of shares; in this, the company does not get any new funds. That is, the company gets money from the IPO, whereas only the shareholders get money from OFS. As an investor, it is important to know what the difference is between OFS and IPO.
What is an IPO?
IPO, or initial public offering, is a process in which a private company brings its shares to the market for sale to the general public for the first time. Its main purpose is to raise capital for the company so that it can expand its business, repay debt, or invest in new projects.
Process of IPO
- Submitting Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP): First, the company files a DRHP with SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India), which contains complete information about the company, financial position, future plans, and risk factors. This document gives investors complete information about the company.
- Determination of price band : After this, the company and its underwriters together decide on a price band. This is the price range at which investors can buy shares.
- Book-building process : After this, the company receives bids (applications) from investors. Investors can bid for shares at any price within the fixed price band. The book-building process helps the company determine what the value of the share should be.
- Allotment of shares : After receiving the bids, the company allocates shares. In this process, it is seen who should get how many shares.
- Listing on Stock Exchange : Finally, the company’s shares get listed on the stock exchange (like NSE or BSE), and then common people and investors can buy and sell the shares in the open market.
An IPO is a good opportunity for investors to be an early part of a company’s growth. If the right company is chosen, there is a possibility of getting good returns from the IPO.
Read Also: What are the Different Types of IPO in India?
What is an OFS?
The full form of OFS is Offer for Sale, and it is a process in which existing promoters or large shareholders sell their share of shares to the public. In this process, the company does not raise new capital, but the already issued shares are sold. The main purpose of OFS is to give the promoters an opportunity to reduce their stake or exit.
Process of OFS
- Determination of floor price : First, the promoters of the company decide the floor price, i.e., the minimum price at which the shares will be sold. This price is usually kept slightly lower than the current market price so as to attract investors.
- Starting the bidding process : Once the floor price is decided, the bidding process begins on the stock exchange. Investors participate in this process and place their bids within the stipulated time frame.
- Allotment of shares : After the bidding, shares are allotted to those investors who placed the highest bids. If the number of bids is high, the allotment is done on a pro rata basis.
- No fresh capital is raised : Since the company does not issue new shares in OFS, it is not considered a means of raising funds. It is just an exit route for shareholders.
- Listing in the market : Finally, the shares sold from OFS get listed on the stock exchange, and investors can buy or sell them in the open market.
The main purpose of OFS is to provide an exit route for promoters, while for investors it is a safe way to buy shares of listed companies.
| Aspect | IPO (Initial Public Offering) | OFS (Offer for Sale) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | The company issues new shares to raise capital. | Promoters or large shareholders sell their stake. |
| Type of Shares | New shares are issued. | Existing shares are sold. |
| Process Complexity | More complex involves strict SEBI scrutiny and approval. | Simpler process conducted via stock exchange bidding. |
| Time Frame | Lengthy process may take several weeks or months. | Quick process can be completed in 1–2 days. |
| Pricing Mechanism | Price band is set (book-building process). | A floor price is set, and bids are invited. |
| Investor Access | Open to all investors both institutional and retail. | Mostly accessible to institutional investors some portion for retail. |
| Dilution Impact | Increases total number of shares, leading to dilution of existing shareholding. | No new shares issued; only ownership changes hands. |
| Regulatory Requirements | Requires detailed SEBI approval and documentation. | Fewer regulatory steps; managed primarily through stock exchange platforms. |
It is clear from this comparison that the purpose of both OFS vs IPO is different, and both the risks and opportunities for applicants are also different. IPO gives new exposure to the company, while in OFS the promoters keep their stake in the stock.
Read Also: What is the Difference Between IPO and Share?
IPO and OFS: Benefits and Limitations
Both IPO (Initial Public Offering) and OFS (Offer for Sale) are important modes of investment in the stock market. While these can be good investment options, it is important to understand the benefits and limitations associated with them so that investors can make informed and strategic decisions.
Benefits of IPO :
- Investors get an opportunity to be a part of the company’s initial growth journey.
- If the company’s performance remains strong, the share price is likely to increase significantly.
- There is a possibility of better returns for long-term investments.
Limitations of IPO :
- There is limited information about new companies, which increases the risk.
- There is a possibility of the share price falling immediately after listing.
- Despite applying for an IPO, getting allotment of shares is not certain.
Benefits of OFS :
- Opportunity to invest in already listed and credible companies.
- The process is fast, transparent and simple, which is convenient for investors.
- Risk is comparatively limited as the company is already active in the market.
Limitations of OFS :
- This process is often more favorable for large institutional investors; participation of retail investors may be limited.
- The company does not receive any new capital, which does not directly impact the company’s expansion plans.
How to invest in IPO and OFS through Pocketful?
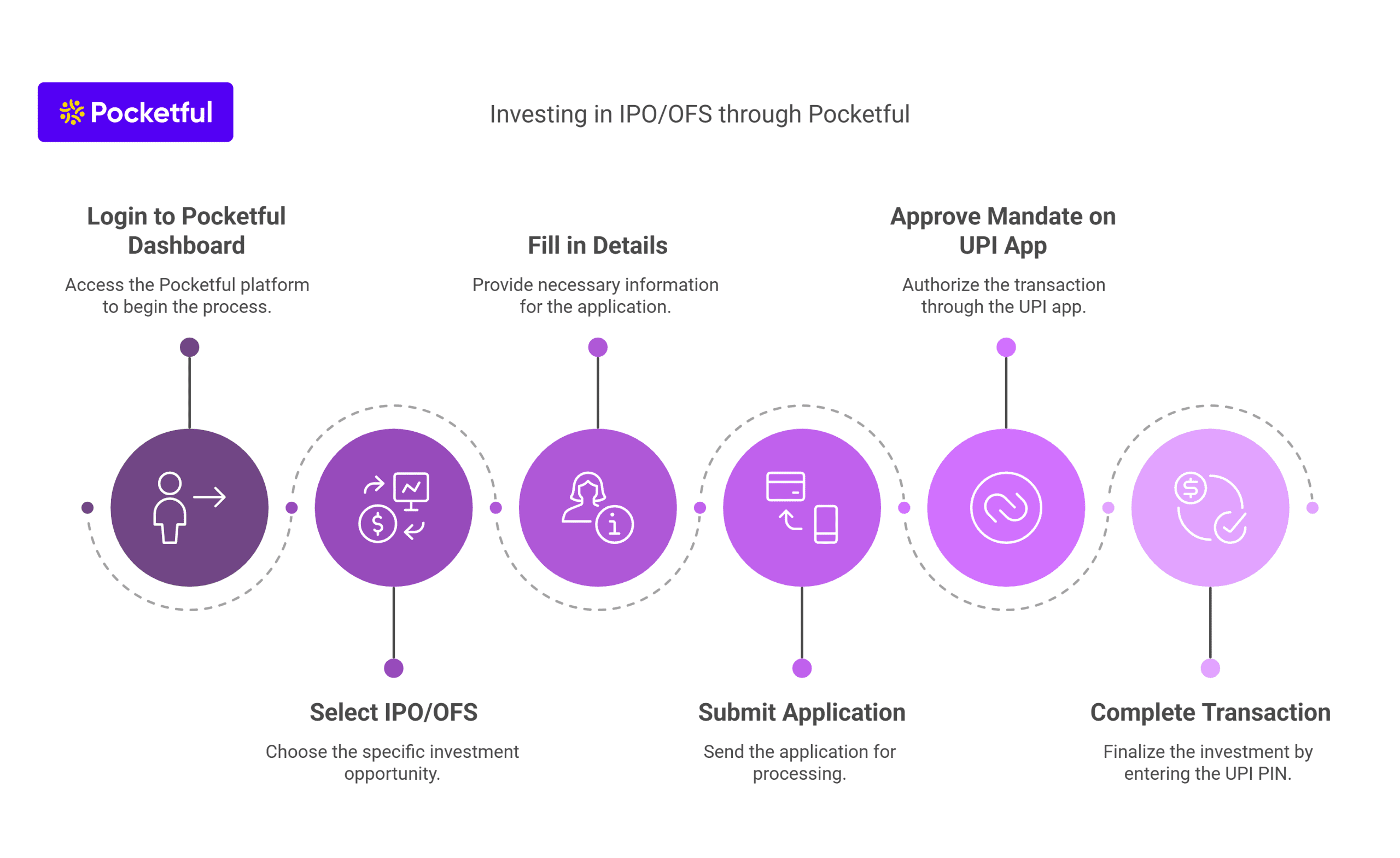
- Login to your Pocketful dashboard and go to the “Current IPOs/OFS” section.
- Select the IPO or OFS you wish to apply for.
- Fill in the required details like number of lots, price, and your UPI ID.
- Read and tick the terms and conditions and click on the Submit button.
- After submitting, a mandate request will appear on your UPI app.
- Open your UPI app, approve the mandate and complete the process by entering the UPI PIN.
Your application will now be successfully submitted. Investing with Pocketful is easy and reliable!
Read Also: Key Difference Between IPO and FPO
Conclusion
IPO and OFS are both important ways of investment, but their purpose and process are different. In IPO, the company raises new capital, while in OFS, the promoters sell their stake. If you want to invest in new growth companies, then an IPO is better. On the other hand, if you want to invest in stable and listed companies with low risk, then OFS is the right option. Before investing, take a decision keeping in mind the company’s condition and your financial goals, so that your investments can be safe and profitable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the full form of IPO and OFS?
IPO means Initial Public Offering, and OFS means Offer for Sale.
Is new capital raised in OFS?
No, in OFS the company does not raise fresh capital; the promoters sell their existing shares.
Can retail investors apply in OFS?
Yes, as per SEBI regulations at least 10% of the OFS is reserved for retail investors.
Which is safer – IPO or OFS?
OFS is considered comparatively safe as the company is already listed.
Is IPO allotment guaranteed?
No, in case of oversubscription of IPO, allotment is done on lucky draw or pro rata basis.
Do I need a demat account for IPO or OFS?
Yes, to invest in both you need to have an active demat account.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.
Article History
Table of Contents
Toggle